NASA Moon Caves

Nasa moon caves –
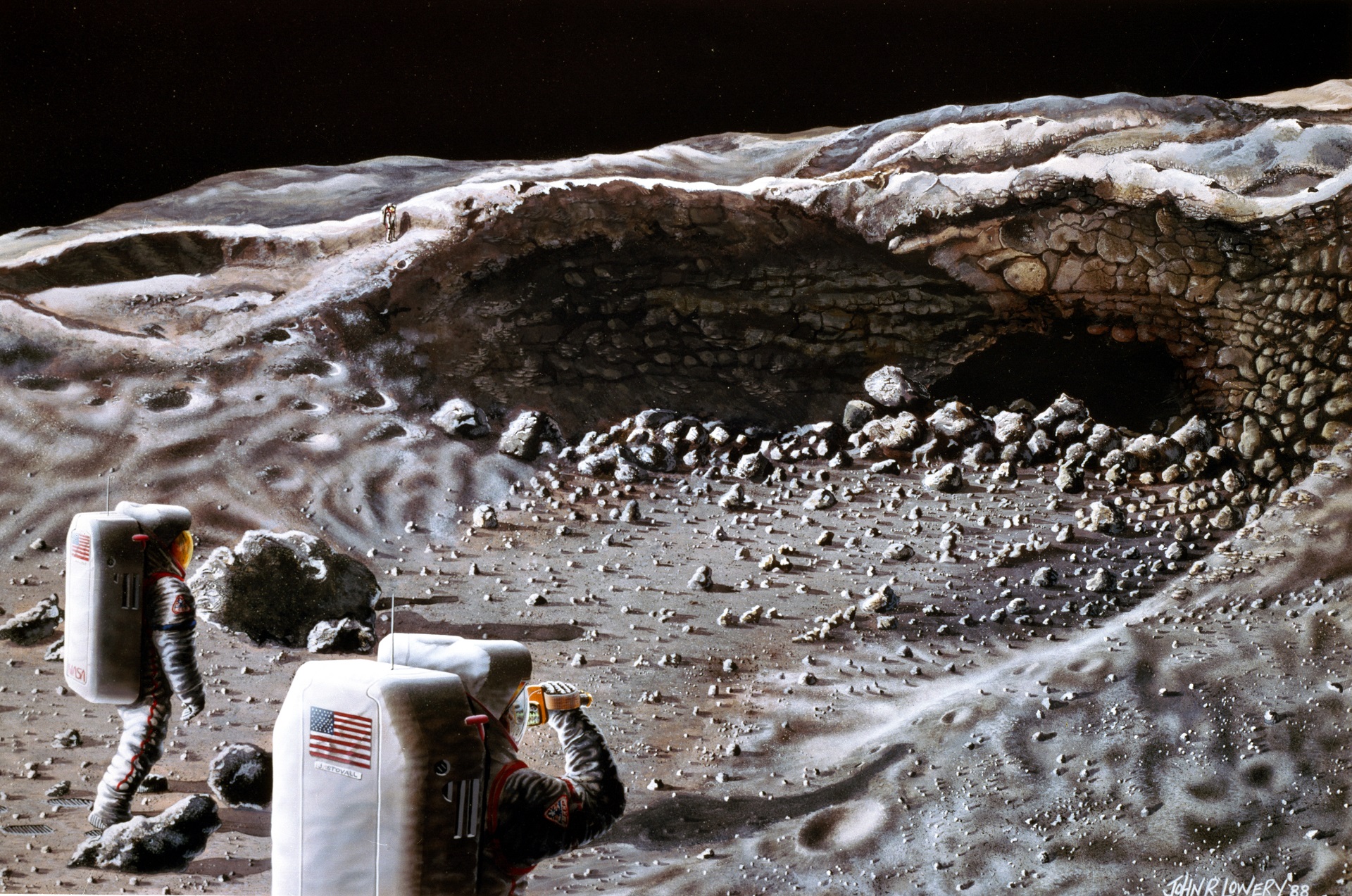
NASA’s exploration of moon caves has been an ongoing endeavor since the 1960s. The first moon cave was discovered in 1969 by the Apollo 11 astronauts, and since then, several other moon caves have been identified and explored.
The mysteries of the moon’s enigmatic caves, with their potential for hidden secrets, evoke a sense of wonder and intrigue. While the complexities of Glenn Youngkin’s religious beliefs may not hold the same cosmic allure, they nonetheless shape his worldview and guide his actions.
Just as the moon’s caves beckon with the promise of discovery, so too do the intricacies of Youngkin’s faith provide insights into the depths of human experience and the uncharted territories of the human spirit.
Moon caves are of great scientific significance because they provide a unique environment that is protected from the harsh conditions on the lunar surface. This makes them ideal for studying the geology and history of the Moon, as well as for conducting experiments that would not be possible on the surface.
Exploration Timeline
- 1969: Apollo 11 astronauts discover the first moon cave.
- 1971: Apollo 14 astronauts explore a second moon cave.
- 1972: Apollo 15 astronauts explore a third moon cave.
- 1973: Apollo 17 astronauts explore a fourth moon cave.
- 2009: The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) discovers a number of new moon caves.
- 2019: The Chang’e 4 lander becomes the first spacecraft to land inside a moon cave.
Scientific Significance
Moon caves are of great scientific significance because they provide a unique environment that is protected from the harsh conditions on the lunar surface. This makes them ideal for studying the geology and history of the Moon, as well as for conducting experiments that would not be possible on the surface.
NASA’s discovery of moon caves has sparked renewed interest in space exploration. The caves, which are thought to be billions of years old, could provide valuable insights into the history of the moon and the solar system. However, some religious groups, such as Glenn Youngkin’s , have expressed concerns about the implications of these discoveries for their beliefs.
They argue that the caves could contain evidence of life on the moon, which would challenge traditional religious teachings about the origins of life on Earth. Despite these concerns, NASA plans to continue exploring the moon caves in the hope of gaining a better understanding of our place in the universe.
Some of the scientific questions that can be addressed by studying moon caves include:
- What is the geological history of the Moon?
- What is the composition of the lunar interior?
- Are there any resources on the Moon that could be used for future human exploration?
- Could moon caves be used as a shelter for future human missions to the Moon?
Challenges and Risks
Exploring moon caves is a challenging and risky endeavor. The caves are often deep and dark, and they can be filled with dangerous gases. Additionally, the lunar surface is covered in a thick layer of dust that can be easily disturbed by human activity.
Some of the challenges and risks associated with exploring moon caves include:
- The caves are often deep and dark, which makes it difficult to navigate and explore.
- The caves can be filled with dangerous gases, such as carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide.
- The lunar surface is covered in a thick layer of dust that can be easily disturbed by human activity, which can create a hazardous environment.
Lunar Cave Features and Characteristics
Moon caves are geological formations found on the Moon. They are typically formed by lava tubes that have collapsed, creating a hollow space. Moon caves can vary in size, from small chambers to large, complex systems that can extend for kilometers.
The environmental conditions within moon caves are unique. The temperature inside a moon cave is typically constant, around -170 degrees Celsius. The atmosphere is thin and composed mostly of carbon dioxide and water vapor. The radiation levels inside a moon cave are also lower than on the surface of the Moon, making them a potential refuge for astronauts and equipment.
Moon caves could potentially contain evidence of life or water. The constant temperature and low radiation levels inside a moon cave could provide a habitable environment for microorganisms. Additionally, the presence of water vapor in the atmosphere of a moon cave suggests that there may be water ice deposits nearby.
Types of Moon Caves
There are two main types of moon caves:
- Lava tubes are formed when lava flows through a tunnel and then cools and solidifies. When the lava flow stops, the tunnel can collapse, creating a cave.
- Mare caves are formed when lava flows into a depression in the lunar surface and then cools and solidifies. The resulting cave is typically circular in shape and has a domed roof.
Geological Formations of Moon Caves
The geological formations of moon caves can vary depending on the type of cave. Lava tubes typically have smooth walls and floors, while mare caves can have more irregular surfaces. The walls of moon caves can be covered in a variety of minerals, including calcite, gypsum, and apatite.
Potential for Finding Evidence of Life or Water in Moon Caves
The potential for finding evidence of life or water in moon caves is high. The constant temperature and low radiation levels inside a moon cave could provide a habitable environment for microorganisms. Additionally, the presence of water vapor in the atmosphere of a moon cave suggests that there may be water ice deposits nearby.
Moon Cave Exploration Technologies and Missions: Nasa Moon Caves
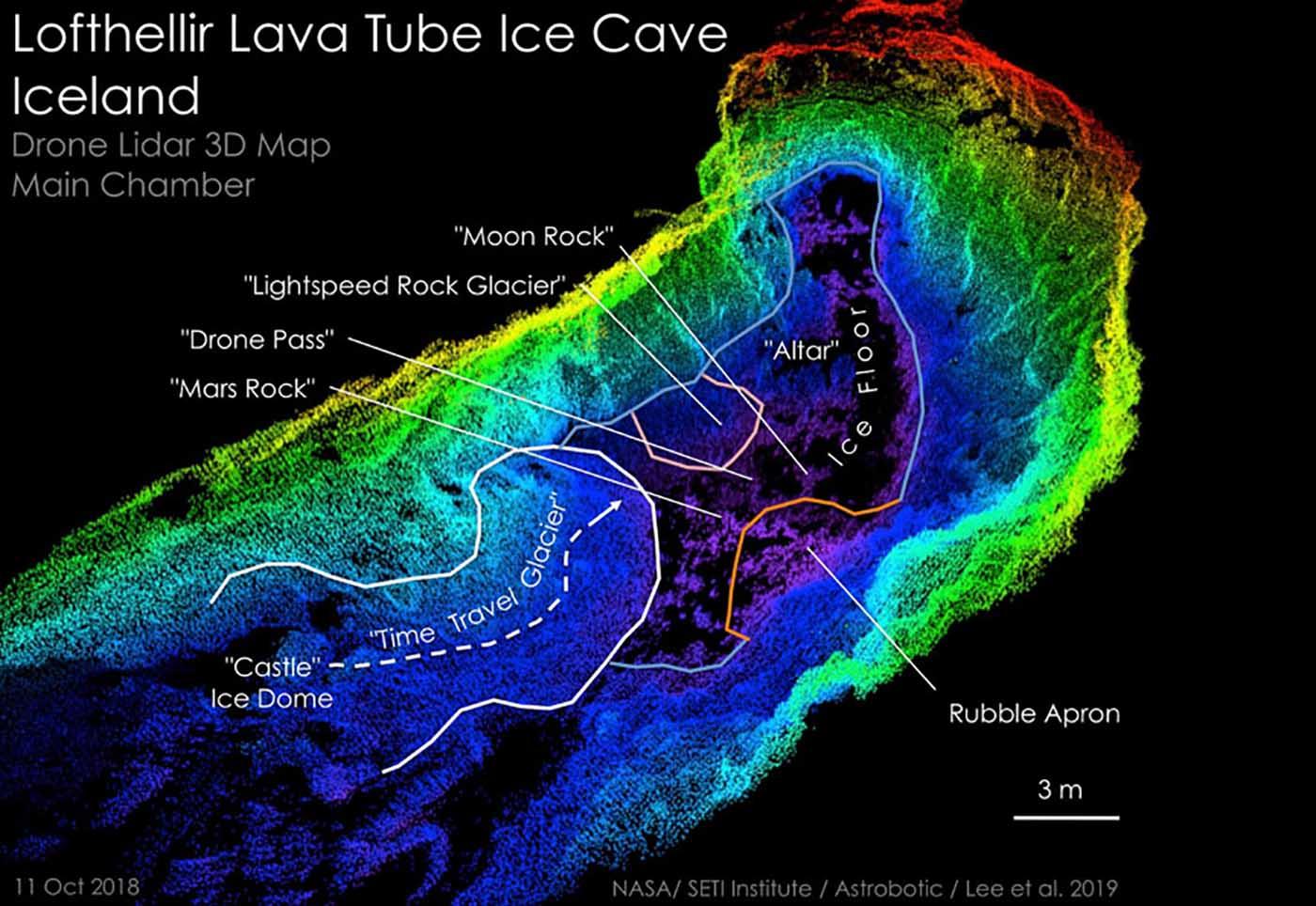
Exploration of moon caves presents unique challenges due to their dark, cold, and potentially hazardous environments. Specialized technologies and equipment are required to safely and effectively navigate and study these caves. Past and planned NASA missions have employed various technologies to explore moon caves, providing valuable insights into their formation, characteristics, and potential scientific significance.
Technologies for Moon Cave Exploration
- Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging): Lidar systems emit laser pulses to measure distances and create detailed maps of cave interiors, revealing their topography, structure, and potential hazards.
- Cameras and Imaging Systems: High-resolution cameras and imaging systems capture visual data, providing detailed views of cave walls, ceilings, and any potential geological features or artifacts.
- Robotic Vehicles and Rovers: Remote-controlled robotic vehicles and rovers can navigate through narrow passages and access difficult-to-reach areas, allowing scientists to explore caves without risking human safety.
- Environmental Sensors: Environmental sensors monitor temperature, humidity, radiation levels, and other environmental conditions within the caves, ensuring the safety of exploration teams and providing data for scientific analysis.
- Sampling and Analysis Equipment: Specialized tools and equipment are used to collect samples of cave materials, such as rocks, dust, and ice, for further analysis and study.
Past and Planned NASA Missions, Nasa moon caves
NASA has conducted several missions to explore moon caves, including:
- Apollo 14 (1971): The Apollo 14 mission included a brief exploration of the Cone Crater, providing the first glimpse into a moon cave.
- Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) (2009-present): The LRO satellite has mapped the lunar surface in high resolution, identifying potential cave openings and providing data for future exploration missions.
- Artemis Program (2025-ongoing): The Artemis program aims to send astronauts back to the moon, including missions to explore moon caves and establish a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
Benefits and Applications of Moon Cave Exploration
Moon cave exploration offers numerous potential benefits and applications for scientific research and future space exploration, including:
- Understanding Lunar History and Formation: Caves can preserve geological records that shed light on the moon’s formation, evolution, and past climate.
- Searching for Life and Biosignatures: Caves provide sheltered environments that could potentially harbor microbial life or preserve evidence of past life on the moon.
- Developing In-Situ Resource Utilization: Caves could provide access to resources such as water ice, which could be used to support future human missions on the moon.
- Testing Technologies and Equipment: Moon caves serve as an ideal testbed for technologies and equipment intended for future missions to Mars and other planetary bodies.